American
![]() f
Manual
Medicine
f
Manual
Medicine
|
American
|
Home Search Somatic Dysfunction Pain referral Trigger points Cranial nerve Spinal nerve Historical
(Dermatological Definition Derived from Dorland's Medical Dictionary and Stedman’s Medical Dictionary with qualification of terms by Author)
The following are descriptions of seven different varieties of flat non-palpable lesions:
1. Macule- a discolored spot, less than 1 cm, which is not elevated above the skin surface.
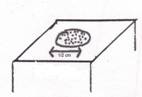
2. Patch- a macule that is 1 cm or more in diameter that differs in color from the surrounding skin and is not elevated above the skin surface.
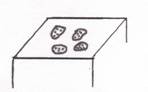
3. Petechiae- a pinpoint, non-raised, perfectly round, purplish-red spot caused by intradermal or submucous hemorrhage.
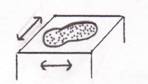
4. Purpura- a small hemorrhage up to about 1cm in diameter in the skin, mucous membrane, or serosal surface, which may be caused by various factors including blood disorders, vascular abnormalities, and trauma. The color is first red, gradually darkens to purple, fades to a brownish yellow, and usually disappears in 2 or 3 weeks. Purpuric lesions may be associated with inflammation, in which case, they present as papular purpura, if not accompanied by inflammation, the hemorrhage is macular.
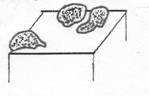
5. Ecchymosis- a small hemorrhagic spot, larger than a petechia, in the skin or mucous membrane forming a non-elevated, rounded or irregular blue or purplish patch.
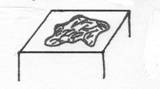
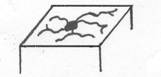
7. Venous “Spider”- radiating lines of capillaries on the leg caused by venous dilatation, but without distinct varicosity.
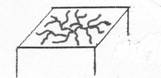
The following are descriptions of seven different varieties of raised solid lesions:
1. Papule- a small, circumscribed, superficial, solid elevation of the skin, usually conically shaped and less than 1 cm in diameter. Causes are inflammation, accumulated secretion or hypertrophy of tissue elements.
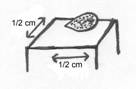
2. Plaque- a superficial, solid, elevated skin lesion equal to or greater than 1 cm in diameter as observed with psoriasis.
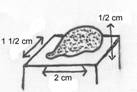
3. Nodule- a small boss (a rounded eminence) or node, which is solid and can be detected by touch, as in a small tumor (breast cancer), trigger point in a muscle or calcification around a joint.
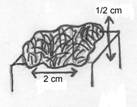
4. Tumor- swelling, one of the cardinal signs of inflammation; morbid enlargement or a new growth of tissue in which the multiplication of cells is uncontrolled and progressive. (neoplasm)
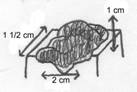
5. Wheal- a smooth, slightly elevated area on the body surface (papule), which is redder or paler than the surrounding skin; it is often attended with severe itching and is usually evanescent (vanishing or quickly passing away), changing its size or shape, or disappearing within a few hours. It is the typical lesion of urticaria; the dermal evidence of allergy and in hypersensitive persons may be provoked by manual or mechanical irritation of the skin. May also be encountered as dermatitis herpetiformis (hives).
6. Scale- a dermatological lesion that exfoliates (a sloughing off) when scraped; made up of keratinized cells.
7. Crust- a formed outer layer, especially an outer layer of solid matter formed by the drying of a bodily exudate or secretion. Observed with ruptured blisters or pustules.
The following are descriptions of five different varieties of raised cystic lesions:
Vesicle- a small circumscribed epidermal elevation, less than 5mm in circumference, usually containing a clear fluid (i.e. Blister).
Pustule- a visible collection of pus within or beneath the epidermis, often in a hair follicle or sweat pore. (i.e. chicken pox, herpes zoster, impetigo, acne conglobata and small pox.)
Bulla- a large vesicle (blister), more than 5mm in circumference containing serous or seropurulent fluid. Can be subepidermal or intraepidermal in nature, sometimes caused by a subcutaneous injection or massive sunburns.
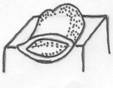
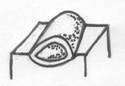
Depressed Lesions
The following are descriptions of four different varieties of depressed lesions:
Atrophy- a wasting away: a diminution or reduction in the size of a cell, tissue, organ or part.
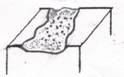
Erosion- a gradual breakdown or very shallow ulceration of the skin, caused by friction or pressure, which involves only the epidermis and heals without scarring.
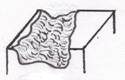
Ulcer- a local defect or excavation of the surface of an organ or tissue, which is produced by the sloughing of inflammatory necrotic tissue. As in the case of a decubitus ulcer.
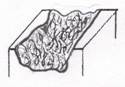
Fissure- exposure of dermis through a narrow crack of epidermis, which is susceptible to microbial invasion.
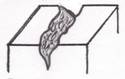
Additional Dermatological Nomenclature and Phenomena
(Dermatological Definition Derived from Dorland's Medical Dictionary, Stedman’s Electronic Medical Dictionary Merriam Webster Medical Dictionary With qualification of terms by Author)
1. Rash - a temporary eruption on the skin, as in urticaria, a drug eruption or viral exanthem (skin eruption).
2. Blanching - turn pale, indicative of ischemia, when predicated by cold, consider Raynaud’s phenomenon or when idiopathic, consider Raynaud’s Disease. Usually accompanied with pain and paresthesia, and most frequently is observed in the hands, nose and ears.
3. Mole - (nevus) the term is also used to designate a pigmented fleshy growth, and applied loosely to any blemish of the skin. While most moles or nevus are benign, a serious condition possibly arising is malignant melanoma. A practitioner should check changes in moles such as irregular growth, itching and darkening of color.
4. Skin tag - (fibroma pendulans) a polypoid outgrowth of both epidermis and dermal fibrovascular tissue, usually benign and occurring on the neck, upper chest, and axillae of middle-aged women.
5. Actinic Keratosis - a scaly patch of skin that develops in predominantly light skinned individuals in areas that have been exposed to excessive sunlight or UV light, such as the face, forearms and hands or shoulders. It is precancerous for squamous cell carcinoma.
6. Basal Cell Carcinoma - a slow growing, invasive, but usually non-metastasizing neoplasm recapitulating normal basal cells of the epidermis or hair follicles, most commonly rising in sun-damaged skin of the elderly and fair-skinned.
7. Kaposi’s Sarcoma - a neoplastic disease affecting the skin and mucous membranes, characterized by the formation of pink to reddish-brown or bluish tumorous plaques, macules, papules or nodules (especially on the lower extremities). Formerly limited primarily to elderly men in whom it followed a benign course, but now being a major and sometimes fatal disease associated with individuals with AIDS.
8. Malignant Melanoma - a malignant neoplasm of melanocytes, arising de novo or from a preexisting benign nevus or lentigo maligna, which occurs most often in the skin but also may involve the oral cavity, esophagus, anal canal, vagina, leptomeninges, conjunctivae or eye. The tumor is classified into four clinical types: superficial spreading melanoma, lentigo maligna melanoma, acral-lentiginous melanoma, and nodular melanoma. Called also melanotic carcinoma, melanoblastoma, and melanocarcinoma.
9. Wart - (verruca) a horny projection on the skin usually of the extremities produced by proliferation of the skin papillae and caused by a papillomavirus. Also known as verruca vulgaris.
Genital wart is located on or around the anus and genital organs. Also called condyloma, condyloma acuminatum or venereal wart.
Plantar wart is located on the sole of the foot and is also known as verruca plantaris or planter’s wart.
10. Bubo - a tender, enlarged, and inflamed lymph node, particularly in the axilla or groin, which frequently weeps puris exudate and is caused by such infections as plague, syphilis, gonorrhea, chancroid, lymphogranuloma venereum, and tuberculosis.
11. Bunion - abnormal prominence of the inner aspect of the first metatarsal head accompanied by bursal formation and resulting in a lateral or valgus displacement of the great toe.
12. Callus - ocalized hyperplasia of the horny layer of the epidermis due to pressure or friction.
13. Exudate - material such as fluid, cells, or cellular debris, which has escaped from blood vessels and has been deposited in tissues or on tissue surfaces, usually as a result of inflammation. An exudate in contrast to a transudate is characterized by a high content of protein, cells, or solid materials derived from cells.
14. Pus - a liquid inflammation product made up of cells and a thin protein rich fluid called liquor puris.
15. Mucus - the free slime of the mucous membranes composed of secretion of the glands along with various inorganic salts, desquamated cells, and leukocytes.
Skin Disorders consider:
Bluish Skin - Anaphylaxis, Atelectasis, Adult Respiratory Distress Syndrome, Arbovirus and Arenavirus, Buerger’s Disease, Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, Cocaine Toxicity, Congenital Heart Disease, Congenital Heart Failure, Cystic Fibrosis, Emphysema, Hypothermia, Hypotension, Kaposi’s Sarcoma, Peripheral Vascular Disease, Pneumonia, Pneumothorax, Pulmonary Edema, Raynaud’s Syndrome, Respiratory Distress Syndrome, Scleroderma, Septic Shock; Bluish skin is also a side effect of Aspirin, Butalbital and Caffeine
Bruise Easily - Anemia, Cirrhosis, Cushing’s Syndrome, Hemophilia, Leukemia, Hodgkin’s Lymphoma, Non Hodgkin’s Lymphoma, Multiple Myeloma, Myelofibrosis, Platelet Function Disorder, Polycythemia Vera, Premenstrual Syndrome, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, Typhoid Fever, Vasculitis, Von Willebrand’s Disease, Wilson Disease; Bruising is also a side effect of Aspirin (aspirin therapy) and numerous other medications
Burns - Chemical Irritant, Electrocution, Fluorine Toxicity, Radiation Therapy, Solar/UV Exposure
Clammy - Anxiety, Bacterial Infection, Cardiac Distress, Common Cold, Hypoglycemia, Hypothermia, Kidney Stone, Malaria, Pancreatitis, Septic Shock, Shock, Viral Infection; Clammy skin is also a side effect of Meperidine Hydrochloride and Morphine
Dry - Contact Dermatitis, Eczema, Heatstroke, Hypervitaminosis A&D, Hypothyroidism, Hypopituitarism, Iodine Toxicity, Psoriasis, Scleroderma, Sjögren’s Syndrome, Vitamin A Toxicity
Growth/Sore does not Heal - Basel Cell Carcinoma, Cancer, Diabetes, Hemophilia, Melanoma, Oral Cancus, Peripheral Vascular Disease, Sinusitis, Varicose Veins
Itching - Anaphylaxis, Anemia, Anthrax, Berylliosis, Breast Cancer, Chemotherapy, Chicken Pox, Chiggers, Cirrhosis, Contact Dermatitis, Dermatomyositis, Eczema, Gallbladder Disorders, Glomerulonephritis, Herpes Zoster, Hodgkin’s Disease, Hypervitaminosis A & D, Leukemia, Liver Failure, Hodgkin’s Lymphoma, Melanoma, Pediculosis (Lice), Pneumoconiosis, Polycythemia Vera, Psoriasis, Renal Failure, Ringworm, Scabies, Sjögren’s Syndrome, Varicose Veins; Itching is also a side effect of Acetaminophen, Tramadol Hydrochloride, Alprazolam, Fluoxetine Hydrochloride, Venlafaxine and Baclofen
Jaundice/Bronzing/Darkening - Addison’s Disease, Anemia, Chemotherapy, Cirrhosis, Empyema, Esophageal Varices, Gallbladder Disorders, Hemochromatosis, Hepatic Carcinoma, Viral Hepatitis, Hypervitaminosis A & D, Liver Failure, Liver Tumors, Myelofibrosis, Pancreatic Cancer, Pancreatitis, Reye’s Syndrome, Septic Shock; Jaundice is also a side effect of Acetaminophen, Anabolic Steroids and numerous other medications.
Mottled - Adult Respiratory Distress Syndrome, Lichen Planus, Melanoma, Peripheral Vascular Disease, Polycythemia Vera, Respiratory Distress Syndrome, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, Vitiligo
Pallor - Acetaminophen Toxicity, Anemia, Endometritis, Frostbite, Hypothermia, Juvenile Arthritis Rheumatoid, Leukemia, Liver Tumors, Digestive Malabsorption, Multiple Myeloma, Myelofibrosis, Platelet Function Disorder, Pulmonary Edema, Raynaud’s Syndrome
Perspiration, excessive - Acetaminophen Toxicity, Acute Stress, AIDS, Alcohol Dementia, Anaphylaxis, Anxiety States, Asthma, Buerger’s Disease, Cocaine Toxicity, Congestive Heart Failure, Cystic Fibrosis, Empyema, Esophageal Rupture, Hyperpituitarism, Hyperthyroidism, Hypoglycemia, Liver Tumors, Lung Abscess, Malaria, Ménière’s Disease, Myocardial Infarction, Pheochromocytoma, Pneumonia, Pulmonary Edema, Pulmonary Embolism, Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy, Renal Vein Thrombosis, Sciatic Nerve Lesions, Sodium Toxicity, Tetanus, Thiamine Deficiency, Tuberculosis, Vitamin D Deficiency
Rash - AIDS, Anaphylaxis, Berylliosis, Biotin Deficiency, Bowen’s Disease, Chemotherapy, Chicken Pox, Chiggers, Dermatomyositis, Discoid Lupus Erythematosus, Eczema, Herpes Zoster, Impetigo, Lice, Lichen Planus, Lyme Disease, Measles, Meningitis, Mixed Connective Tissue Disease, Niacin Deficiency, Pneumoconiosis, Polymyositis, Psoriasis, Psoriatic Arthritis Erythrasma, Rheumatic Fever, Rheumatoid Arthritis Juvenile, Ringworm, Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever, Roseola, Rubella, Sarcoidosis, Scabies, Selenium Toxicity, Septic Shock, Strep Infection, Syphilis, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, Tinea Versicolor, Toxemia of Pregnancy, Toxic Shock Syndrome, Typhoid Fever; Rash is also a side effect of Acetaminophen, Alprazolam and numerous other medications.
Red - Acne Rosacea, Acute Lymphangitis, Alcoholism, Anaphylaxis, Anemia, Atopic Dermatitis, Bacterial Tenosynovitis, Burns (First Degree), Candidiasis, Carbunculosis, Carcinoid Tumors, Carcinoid Syndrome, Cellulitis, Chemical Irritant, Cirrhosis, Contact Dermatitis, Cushing’s Syndrome, Decubitus Ulcers, Dermatomyositis, Ecthyma, Eczema, Erysipelas, Folliculitis, Frostbite, Furunculitis, Heatstroke, Histamine Headaches, Hyperemia, Impetigo, Kaposi’s Syndrome, Lymphangitis, Menopause Syndrome, Mitral Stenosis, Pemphigus, Pheochromocytoma, Pityriasis Rosea, Psoriasis, Pulmonary Emphysema, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Ringworm, Roseola, Rubella, Scleroderma, Solar Exposure, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, Toxic Shock Syndrome, Varicose Ulcers, Vitamin C Deficiency, Vitamin E Deficiency, Whiplash; Red discoloration is also a side effect of Acetaminophen, Tramadol Hydrochloride, Felodipine, Verapamil Hydrochloride
Scaly - Contact Dermatitis, Eczema, Erythrasma, Hypervitaminosis A & D, Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma, Peripheral Vascular Disease, Psoriasis, Riboflavin Deficiency, Ringworm, Scabies, Sjögren’s Syndrome, Syphilis, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, Tinea Versicolor, Varicose Veins, Vitamin A Toxicity, Vitamin E Deficiency
Scar - Acne Conglobata, Bulimia, Burns (Post Third Degree), Discoid Lupus Erythematosus, Ecthyma, Herpes Simplex, Herpes Zoster, Incisional Hernia, Previous Severe Trauma, Surgical Adhesions, Vitamin C Deficiency
Ulcers - Atherosclerosis, Basal Cell Carcinoma, Decubitus Ulcers, Genital Herpes, Herpes Simplex, Herpes Zoster, Raynaud’s Syndrome, Reiter’s Syndrome, Varicose Ulcers, Varicose Veins
© Copyright